Enzymes are at the heart of many applications at Lesaffre, from the production of biofuels, petroleum substitutes for the manufacture of plastic materials, to molecules of therapeutic interest. Protein Engineering has a crucial role in these applications. A new tool using Artificial intelligence is being developed by the Digital & Data Department and the BioData and BioEngineering teams in LIST (Lesaffre Institute of Science and Technology).
What is protein engineering?
Protein engineering is the process of intentionally modifying the structure of proteins to improve their properties or generate new proteins. A protein’s structure is determined by its sequence, which refers to the specific order of “building blocks” called amino acids that make up the protein. Sequence variants are modified versions of proteins where their amino acid sequence has been deliberately altered by genome editing. Protein engineering involves exploring different sequence variants to optimize a protein’s properties, such as its activity, stability or efficiency.
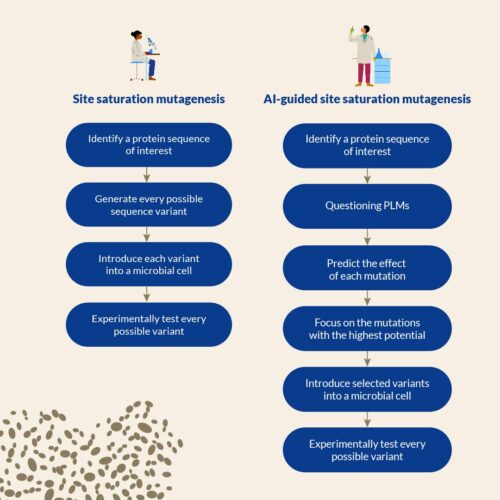
A possible approach to Protein engineering, offered in particular by the Recombia technology, is called Site Saturation Mutagenesis. It involves generating and experimentally testing every possible alternative amino acid at each position of an initial protein sequence. However, while seducing by its systematic nature, this method requires significant manpower and often leads to testing many irrelevant variants.
How can protein engineering be improved with AI?
One promising technological advancement in AI is the use of Protein Language Models (PLMs).
A PLM is a computer algorithm powered by machine learning that analyzes vast amounts of protein sequence data to provide valuable insights into the structure-function relationships of proteins. Just as a GPT model like ChatGPT analyzes the letters of the alphabet to understand and predict textual language, a PLM analyzes amino acids – the ‘letters’ of the language of life – to model protein behavior and predict how specific modifications to a protein’s sequence might affect its stability and function.
PLMs enable scientists to optimize protein performance for various applications and are getting a considerable interest in the scientific community. One of the key features of PLMs is their ability to identify new sequence variations that may otherwise be difficult to identify using traditional methods.
What are the benefits?
AI-guided protein engineering leveraging Protein Language Models (PLMs) provides data-driven insights that facilitate informed decision-making on protein optimization strategies.
In the context of Site Saturation Mutagenesis, PLMs enable researchers to screen mutations in silico and prioritize protein variants for experiments, reducing the workload for manual testing and making the variant selection process more cost-efficient.
Beyond Site Saturation Mutagenesis, AI and PLMs present great opportunities to further accelerate protein engineering, ultimately leading to faster delivery of better products.
When will this tool be launched?
The D&D Team released the first Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for this project beginning of July. This tool will be leveraged by the BioEngineering and BioData teams of the LIST in various metabolic engineering projects related to precision fermentation.